
The Michigan Anticoagulation Quality Improvement Initiative (MAQI2) found that patients taking warfarin in combination with aspirin had twice the rate of bleeding with no clear clinical benefit, similar to other published literature. Over one-third of patients taking this combination did not have a clear reason to be taking aspirin. For patients already on lifelong warfarin treatment, guidelines recommend against adding aspirin therapy following TAVR in the absence of a recent PCI. By developing systems to identify patients on inappropriate aspirin and coordinating with providers, sites have reduced inappropriate aspirin use by 50% in participating clinics since 2018, resulting in fewer bleeding events.
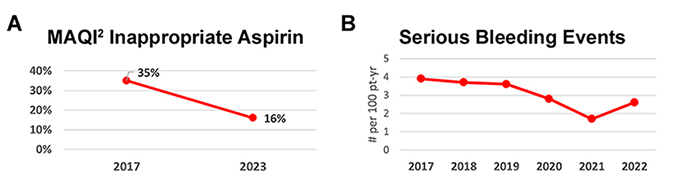
MAQI2 is a collaborative of anticoagulation clinics across the State of Michigan seeking to improve the safety, quality of care and outcomes of patients requiring anticoagulation. Its initiative uses data to identify cases of possible inappropriate aspirin prescription, followed by direct contact with the prescriber, who then makes the final clinical decision about whether to continue aspirin.
MAQI2 began its work in 2018, targeting patients with no history of coronary artery disease. It expanded its reach to patients >12 months post-PCI and will continue to broaden its population in 2024 and 2025 by focusing on valve patients.