
A recent analysis of BMC2 and MISHC data compared to national registry data partners revealed a variety of critical-to-quality measures on which Michigan participants excel.
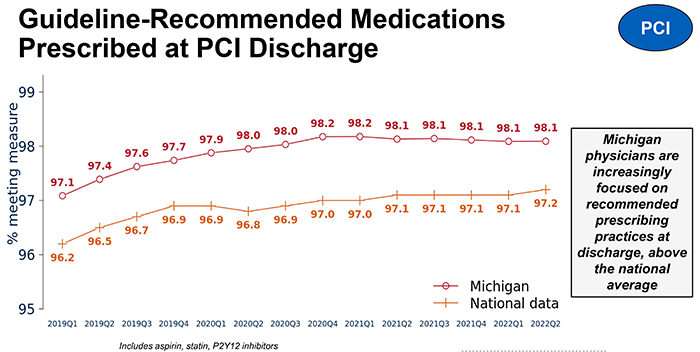
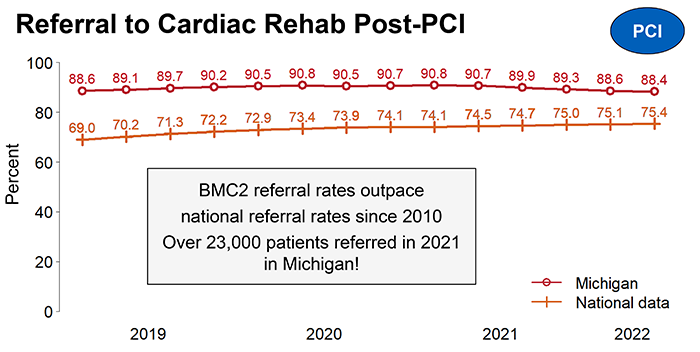
In patients who have had PCI, BMC2 data demonstrate that Michigan physicians increasingly focus on prescribing guideline-recommended medications that reduce cholesterol and prevent blood clots and do so consistently above the national average. BMC2 hospitals also have a steady low blood transfusion rate after PCI over time and at rates below the national average. Additionally, BMC2 surpasses the nation at referral to cardiac rehabilitation; a 90% referral rate in Michigan translates to over 23,000 patients referred to cardiac rehab each year. These interventions contribute to improved long-term health outcomes and reduction in hospital readmissions.
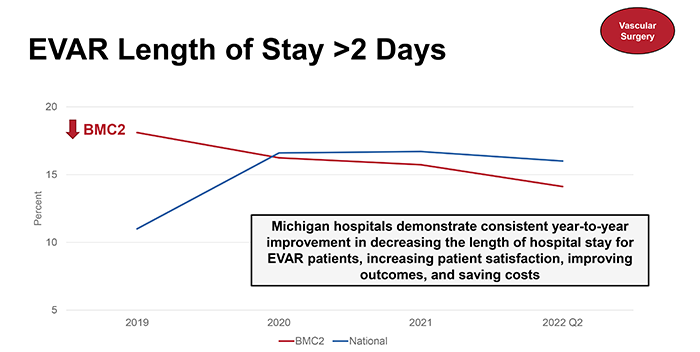
Similarly, among VS patients, BMC2 hospitals prescribe guideline-recommended medications at a higher rate than national counterparts. Michigan hospitals demonstrate consistent year-to-year improvement in decreasing the length of hospital stay for endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) patients, increasing patient satisfaction, improving outcomes, and saving costs.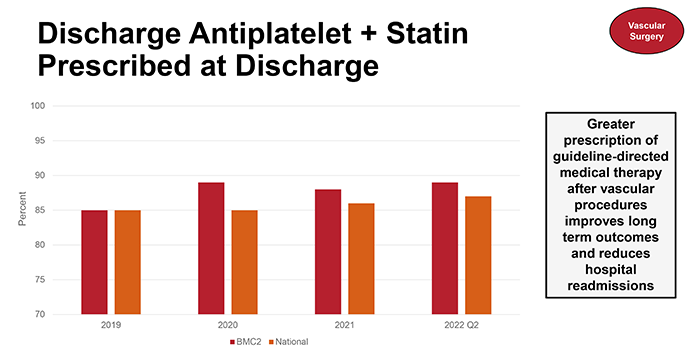
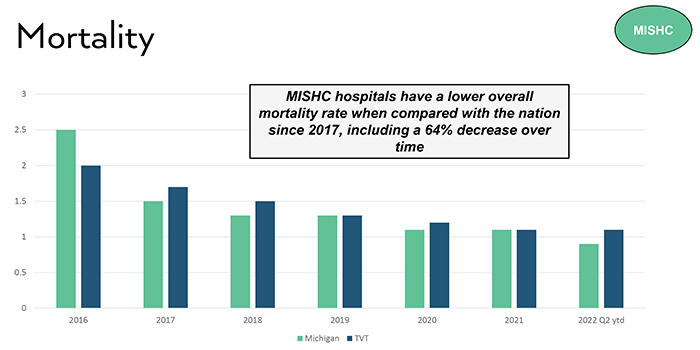
MISHC hospitals have a lower overall death rate when compared with the nation since 2017, including a 64% decrease over time. MISHC hospitals maintain a steady decreasing rate of blood transfusions, avoiding more than 4000 transfusions. This result was attained when MISHC set a statewide goal, issued best practice protocols and quarterly data reports, and convened consortium meeting presentations and discussions. 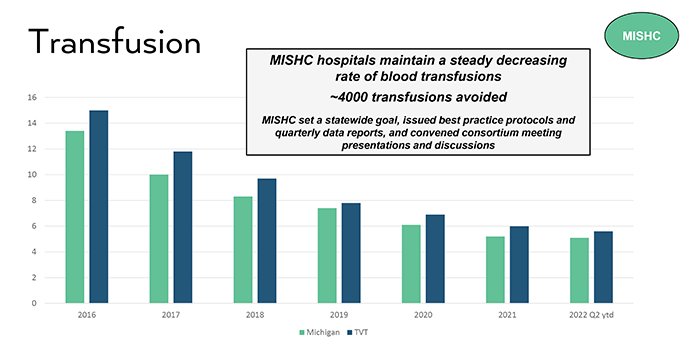
The power of CQIs is evident in BMC2 performance on key measures of quality when compared to national rates. This is supported through research. A recent article by Beaulieu et al. (3) demonstrated that participation in BMC2 is a key contributor toward increased adherence to best practices and hospital performance improves the longer they are members. Patients in Michigan clearly benefit from the strength of the collaborative work of BMC2 through improvements in care and outcomes.